China Increases Defense Budget by 7.2% Amid Rising Tensions
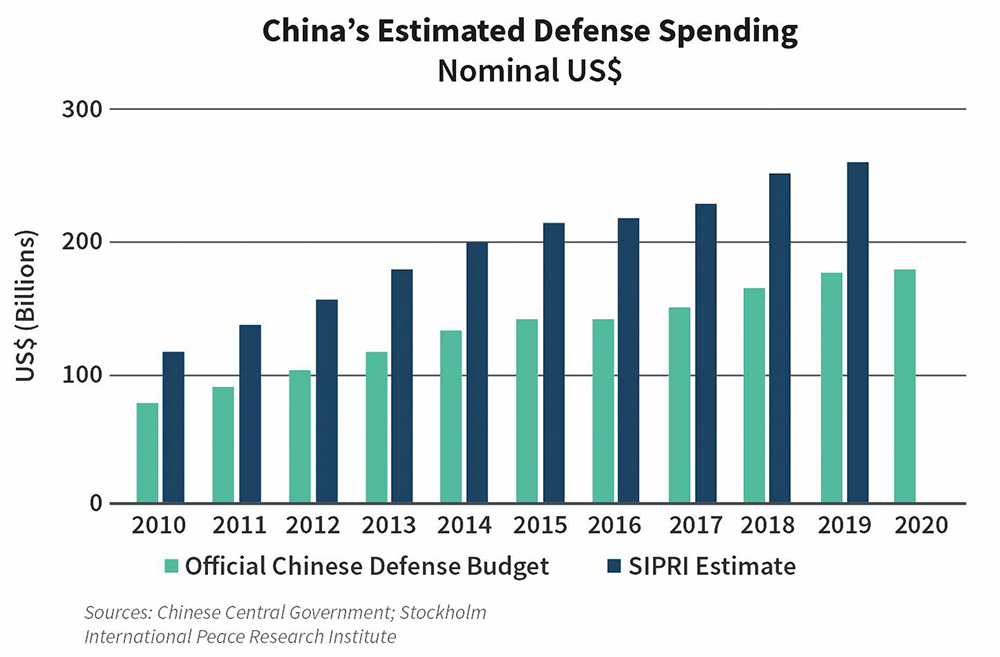
On Tuesday, China unveiled a 7.2% increase in its defense budget, currently the world’s second-largest after the United States, totaling 1.6 trillion yuan ($222 billion), a figure reminiscent of last year’s increment.
Rising tensions with the U.S., Taiwan, Japan, and neighboring countries with conflicting claims in the strategically significant South China Sea are believed to be driving the growth in advanced military technologies, spanning from stealth aircraft to aircraft carriers and an expanding array of nuclear weaponry.
The officially disclosed budget, presented during the commencement of the annual legislative session, represents only a portion of the spending by the People’s Liberation Army (PLA), the military branch of the ruling Communist Party. This includes outlays for research and development as well as acquisitions of foreign weaponry.
Premier Li Qiang, addressing the assembly comprised of nearly 3,000 carefully chosen participants known for their staunch loyalty to the Communist Party and its leader, Xi Jinping, affirmed the commitment to providing robust financial support to modernize national defense and armed forces across all domains. This aims to fortify and enhance integrated national strategies and strategic capabilities.
China’s Defense Budget Surges Amid Economic Challenges and Regional Ambitions

Since 2015, China’s defense budget has more than doubled, despite a considerable slowdown in the country’s economic growth rate. Nevertheless, China remains steadfast in its ambition to challenge the U.S. and its Asian allies such as Japan, South Korea, the Philippines, and Australia on territorial disputes, regional influence, and global governance.
During the 2000s, China experienced double-digit percentage increases in its defense budget. However, this growth began to decelerate as the once-booming economy reached a plateau. Premier Li, in his address, set the GDP growth target for this year at 5%, while acknowledging the challenges in achieving it.
China’s economy is grappling with issues such as high youth unemployment and a declining real estate market. This decline follows the inability of developers, who had taken out substantial bank loans, to repay their debts or fulfill their obligations to buyers who had invested their life savings in purchasing homes.
Beijing’s Global Ambitions Persist Despite Tensions
Despite challenges, Beijing’s global aspirations remain undeterred. Priorities such as asserting control over the self-governing island of Taiwan, addressing border disputes with India, and consolidating control over islands in the East China and South China Seas remain at the forefront of China’s agenda.
In a recent concerning development, Chinese coast guard vessels reportedly obstructed Philippine vessels near a disputed shoal in the South China Sea, resulting in a minor collision, according to the Philippine coast guard.
Philippine security officials have accused Chinese coast guard ships and suspected militia vessels of engaging in hostile actions, including blocking Philippine vessels and using water cannons and military-grade lasers that temporarily blinded Filipino crew members, during incidents at sea last year.
These actions contribute to China’s increasingly intense rivalry with the United States across political, economic, military, and technological domains. This rivalry has resulted in punitive measures such as tariffs and travel bans on Chinese officials, followed by retaliatory actions by Beijing. Additionally, China’s support for Russia and its refusal to condemn the invasion of Ukraine have further strained relations with Washington.
In 2022, China’s defense spending was equivalent to 1.6% of its GDP, whereas the United States allocated 3.5% of its GDP to defense during the same period, as reported by the World Bank. While the U.S. defense budget has decreased to approximately 12% of government spending, it’s challenging to determine the exact proportion China allocates to defense due to numerous civilian-military collaboration projects spanning technology, business, and real estate.
Moreover, China consistently deploys ships and aircraft near Taiwan on a daily basis. This strategy aims to degrade the equipment and morale of the Taiwanese armed forces and reinforce the message that Taiwan’s reunification with the mainland is inevitable, even if it requires the use of force.











Comments 7